Content
- How Accounting Software Can Streamline Your Depreciating Asset Calculations
- Capital Cost Recovery in the OECD since 2000
- Averaging conventions
- Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
- Depreciation Definition and Calculation Methods
- What Is Depreciation in Business?
In reality, each brand and model of a car loses its value at a slightly different rate; formally, we say, it has its car depreciation rate. Still, you can use this calculator to show you what the value will be more or less after a specific time has elapsed. In this example, the government allows investment in machinery to be deducted on a straight-line method of 12.5 percent for eight years.
Tara Corporation, a calendar year taxpayer, was incorporated and began business on March 15. During December, it placed property in service for which it must use the mid-quarter convention. This is a short tax year of other than 4 or 8 full calendar months, so it must determine the midpoint of each quarter. If your property has a carryover basis because you acquired it in a nontaxable transfer such as a like-kind exchange or involuntary conversion, you must generally figure depreciation for the property as if the transfer had not occurred. However, see Like-kind exchanges and involuntary conversions, earlier, in chapter 3 under How Much Can You Deduct; and Property Acquired in a Like-kind Exchange or Involuntary Conversion next. You reduce the adjusted basis ($288) by the depreciation claimed in the fourth year ($115) to get the reduced adjusted basis of $173.
How Accounting Software Can Streamline Your Depreciating Asset Calculations
See the Instructions for Form 1065 for information on how to figure partnership net income (or loss). However, figure taxable income without regard to credits, tax-exempt income, the section 179 deduction, and guaranteed payments under section 707(c) of the Internal Revenue Code. Each partner adds the amount allocated from partnerships (shown on Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), Partner’s Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc.) to their nonpartnership section 179 costs and then applies the dollar limit to this total. To determine any reduction in the dollar limit for costs over $2,700,000, the partner does not include any of the cost of section 179 property placed in service by the partnership. After the dollar limit (reduced for any nonpartnership section 179 costs over $2,700,000) is applied, any remaining cost of the partnership and nonpartnership section 179 property is subject to the business income limit.

However, if you change the property’s use to use in a business or income-producing activity, then you can begin to depreciate it at the time of the change. You place the property in service in the business or income-producing activity on the date of the change. You begin to depreciate your property when you place it in service for use Depreciation Definition And Calculation Methods in your trade or business or for the production of income. You stop depreciating property either when you have fully recovered your cost or other basis or when you retire it from service, whichever happens first. For more information on the records you must keep for listed property, such as a car, see What Records Must Be Kept?
Capital Cost Recovery in the OECD since 2000
Unit of production method needs the number of units used during production. Here is a graph showing the book value of an asset over time with each different method. For example, at the beginning of the year, the asset has a remaining life of 8 years. The following year, the asset has a remaining life of 7 years, etc.
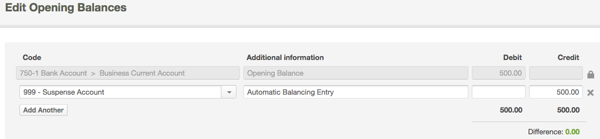
In the case of a partnership, S corporation, or consolidated group, the election is made by the partnership, by the S corporation, or by the common parent of a consolidated https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/ group, respectively. You multiply the reduced adjusted basis ($288) by the result (40%). You multiply the reduced adjusted basis ($480) by the result (28.57%).
Averaging conventions
For a detailed discussion of passenger automobiles, including leased passenger automobiles, see Pub. If you dispose of GAA property in a qualifying disposition, you can choose to remove the property from the GAA. A qualifying disposition is one that does not involve all the property, or the last item of property, remaining in a GAA and that is described by any of the following.
The recovery period begins on the placed in service date determined by applying the convention. The remaining recovery period at the beginning of the next tax year is the full recovery period less the part for which depreciation was allowable in the first tax year. The depreciation for the computer for a full year is $2,000 ($5,000 × 0.40). You placed the computer in service in the fourth quarter of your tax year, so you multiply the $2,000 by 12.5% (the mid-quarter percentage for the fourth quarter). The result, $250, is your deduction for depreciation on the computer for the first year. If this convention applies, the depreciation you can deduct for the first year that you depreciate the property depends on the month in which you place the property in service.